rooting代码分析
socket相关
Af_unix域socket通信
本机内进程间通信可以使用socket的AF_UNIX域通信,是一种本地IPC,类似于管道,依赖路径名称标识发送方和接收方。
int socket(int af, int type, int protocol);
af为地址族,type为套接字类型,protocol为使用TCP还是UDP,执行正确返回套接字描述符,错误则返回-1
socket_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
表示创建一个用于本机进程间通信的流式套接字,协议自动选择TCP,最后一个0表示自动推演,是一种简化的写法,比如
int tcp_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); //创建TCP套接字
int udp_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); //创建UDP套接字
fcntl(socket_fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC)
对socket_fd这个描述符设置有效除非执行exec类型函数
fcntl是对已打开的文件描述符做控制操作
F_SETFD设置文件描述符标志
c语言用法
#define SERVER_DIR "/data/mydaemon"
#define SERVER_LOC SERVER_DIR "/server"
c语言中两个字符串是可以通过空格连接的,故以上语句等价于
#define SERVER_LOC "/data/mydaemon/server"
linux系统函数
int unlink(const char * pathname);
删除指定的文件
int previous_umask = umask(0)
umask是用来设置用户创建文件的默认权限的,用一个例子来说明
1、文件最大权限 rwx rwx rwx,对应777
2、umask值如为2, --- --- -w-
3、目录权限 rwx rwx r-x,对应775,这就是目录创建的缺省权限
4、对于文件来说,创建时不能具有执行权限,只要拿掉相应执行权限比特即可,rw- rw- r--,对应664,这就是文件创建缺省权限
如umask设置为0,目录创建权限777,文件创建权限666
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
复制旧的文件描述符到新的文件描述符,如果新的已经被使用,则会先把它关闭
/dev/urandom是linux提供的随机伪设备,提供不为空的随机字节数据流,urandom不依赖系统中断,也不会造成进程忙等待,数据随机性也不高, 而/dev/random则依赖中断,会造成进程忙,随机性高
/dev/tty如果一个控制台有一个终端的话,那么这个文件就是对应的当前的这个控制终端的别名。当程序打开此文件是, Linux会自动将它重定向到一个终端窗口
项目分析
SimpleSU项目代码结构如下:
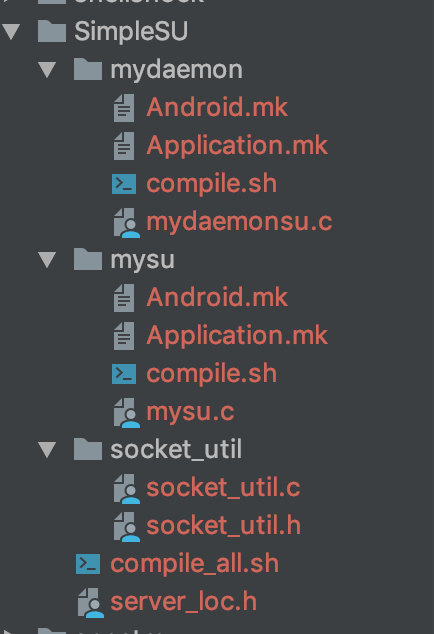
主要是三个文件,一个服务端mydaemonsu.c,一个客户端mysu.c,还有一个socket函数文件socket_util.c
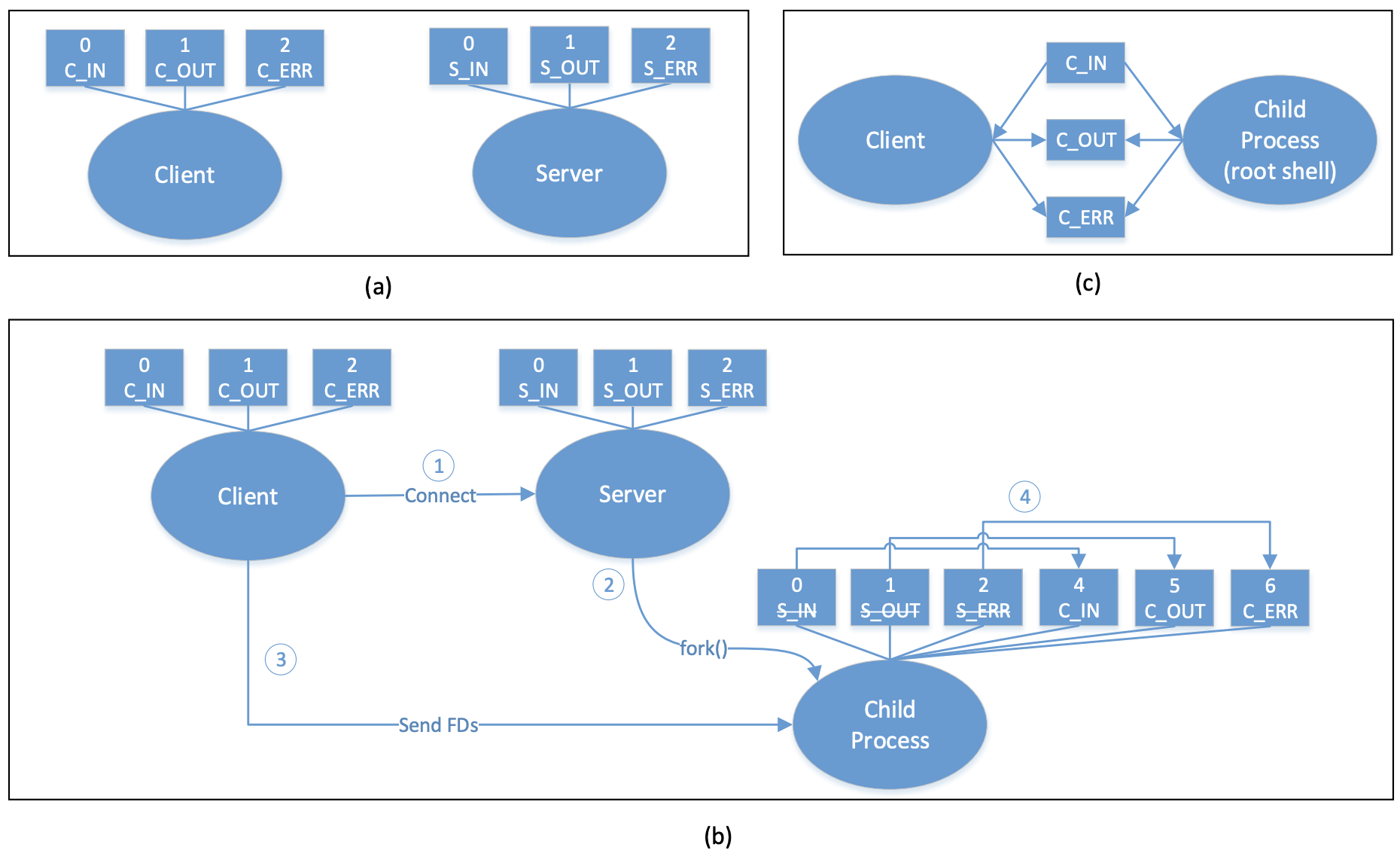
客户端获取另一个进程输入输出设备过程: 开始时,客户端和服务器都运行在各自进程,客户端只有普通权限,服务器有root
权限,图b展示了客户端获取root权限过程:
1、客户端用socket连接服务器
2、收到请求后,服务器fork一个子进程root运行,子进程继承了所有服务器的I/O设备
3、客户端发送文件描述符给子进程,这些描述符分别用4、5、6保存
4、子进程重定向设备描述符,现在客户端进程和子进程共享设备描述符了
socket_util.c:
#include "socket_util.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h> //socket() bind() listen() accept()
#include <fcntl.h> //fcntl()
#include <errno.h> //errno
#include <limits.h> //PATH_MAX
#include <string.h>
#define LOGE(fmt,args...) fprintf(stderr, fmt, ##args)
#define PLOGE(fmt,args...) LOGE(fmt " failed with %d: %s", ##args, errno, strerror(errno))
/*
* Receive a file descriptor from a Unix socket.
* Contributed by @mkasick
*
* Returns the file descriptor on success, or -1 if a file
* descriptor was not actually included in the message
*
* On error the function terminates by calling exit(-1)
*/
int recv_fd(int sockfd) {
// Need to receive data from the message, otherwise don't care about it.
char iovbuf;
struct iovec iov = {
.iov_base = &iovbuf,
.iov_len = 1,
};
char cmsgbuf[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(int))];
struct msghdr msg = {
.msg_iov = &iov,
.msg_iovlen = 1,
.msg_control = cmsgbuf,
.msg_controllen = sizeof(cmsgbuf),
};
if (recvmsg(sockfd, &msg, MSG_WAITALL) != 1) {
goto error;
}
// Was a control message actually sent?
switch (msg.msg_controllen) {
case 0:
// No, so the file descriptor was closed and won't be used.
return -1;
case sizeof(cmsgbuf):
// Yes, grab the file descriptor from it.
break;
default:
goto error;
}
struct cmsghdr *cmsg = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&msg);
if (cmsg == NULL ||
cmsg->cmsg_len != CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int)) ||
cmsg->cmsg_level != SOL_SOCKET ||
cmsg->cmsg_type != SCM_RIGHTS) {
error:
LOGE("unable to read fd");
exit(-1);
}
return *(int *)CMSG_DATA(cmsg);
}
/*
* Send a file descriptor through a Unix socket.
* Contributed by @mkasick
*
* On error the function terminates by calling exit(-1)
*
* fd may be -1, in which case the dummy data is sent,
* but no control message with the FD is sent.
*/
void send_fd(int sockfd, int fd) {
// Need to send some data in the message, this will do.
struct iovec iov = {
.iov_base = "",
.iov_len = 1,
};
struct msghdr msg = {
.msg_iov = &iov,
.msg_iovlen = 1,
};
char cmsgbuf[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(int))];
if (fd != -1) {
// Is the file descriptor actually open?
if (fcntl(fd, F_GETFD) == -1) {
if (errno != EBADF) {
goto error;
}
// It's closed, don't send a control message or sendmsg will EBADF.
} else {
// It's open, send the file descriptor in a control message.
msg.msg_control = cmsgbuf;
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(cmsgbuf);
struct cmsghdr *cmsg = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&msg);
cmsg->cmsg_len = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
cmsg->cmsg_level = SOL_SOCKET;
cmsg->cmsg_type = SCM_RIGHTS;
*(int *)CMSG_DATA(cmsg) = fd;
}
}
if (sendmsg(sockfd, &msg, 0) != 1) {
error:
PLOGE("unable to send fd");
exit(-1);
}
}
int read_int(int fd) {
int val;
int len = read(fd, &val, sizeof(int));
if (len != sizeof(int)) {
LOGE("unable to read int: %d", len);
exit(-1);
}
return val;
}
void write_int(int fd, int val) {
int written = write(fd, &val, sizeof(int));
if (written != sizeof(int)) {
PLOGE("unable to write int");
exit(-1);
}
}
char* read_string(int fd) {
int len = read_int(fd);
if (len > PATH_MAX || len < 0) {
LOGE("invalid string length %d", len);
exit(-1);
}
char* val = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len + 1));
if (val == NULL) {
LOGE("unable to malloc string");
exit(-1);
}
val[len] = '\0';
int amount = read(fd, val, len);
if (amount != len) {
LOGE("unable to read string");
exit(-1);
}
return val;
}
void write_string(int fd, char* val) {
int len = strlen(val);
write_int(fd, len);
int written = write(fd, val, len);
if (written != len) {
PLOGE("unable to write string");
exit(-1);
}
}
/*provided by Zhuo Zhang @ Syracuse University*/
//pass dummy message from client to server and wait for response
void handshake_client(int socket) {
FILE* rand_fp = fopen("/dev/urandom", "r");
int ack_num;
fread(&ack_num, sizeof(int), 1, rand_fp);
fclose(rand_fp);
write_int(socket, ack_num);
int back_num = read_int(socket);
if (back_num != ack_num) {
shutdown(socket, SHUT_RDWR);
close(socket);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
/*provided by Zhuo Zhang @ Syracuse University*/
//receive a dummy message from client and send it back
void handshake_server(int socket) {
int ack_num = read_int(socket);
write_int(socket, ack_num);
}
mydaemonsu.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h> //socket() bind() listen() accept() AF_UNIX
#include <fcntl.h> //fcntl()
#include <string.h> //strerror()
#include <errno.h> //errno
#include <sys/un.h> //struct sockaddr_un
#include <sys/stat.h> //umask() mkdir()
#include <stdbool.h> //bool true false
#include "../socket_util/socket_util.h"
#include "../server_loc.h"
#define ERRMSG(msg) fprintf(stderr, "%s", msg)
#define DEFAULT_SHELL "/system/bin/sh"
#define SHELL_ENV "SHELL=/system/bin/sh"
#define PATH_ENV "PATH=/system/bin:/system/xbin"
#define APP_PROCESS "/system/bin/app_process_original"
extern char** environ;
//create a UNIX domain socket and return its file descriptor
int creat_socket() {
int socket_fd;
struct sockaddr_un sun;
//open socket
socket_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (socket_fd < 0) {
ERRMSG("failed to open socket\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//set the socket file descriptor
//with flag FD_CLOEXEC, socket_fd will stay valid through fork()
//but will be destroyed by all exec family functions (e.g. execve())
if (fcntl(socket_fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC)) {
ERRMSG("failed to fcntl\n");
goto err;
}
//set struct sockaddr_un
/*
struct sockaddr_un {
sa_family_t sun_family; //AF_UNIX
char sun_path[108]; //pathname
};
*/
memset(&sun, 0, sizeof(sun));
sun.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strncpy(sun.sun_path, SERVER_LOC, sizeof(sun.sun_path));
//get rid of potential existing file due to previous error
unlink(sun.sun_path);
unlink(SERVER_DIR);
//backup current umask
//and change umask to allow all permissions
int previous_umask = umask(0);
//make new server path
mkdir(SERVER_DIR, 0777);
//bind socket
if (bind(socket_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&sun, sizeof(sun)) < 0) {
ERRMSG("failed to bind socket\n");
goto err;
}
//restore umask
umask(previous_umask);
//start listening on the socket
if (listen(socket_fd, 10) < 0) {
ERRMSG("failed to listen\n");
goto err;
}
return socket_fd;
err:
close(socket_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//the code executed by the child process
//it launches default shell and link file descriptors passed from client side
int child_process(int socket, char** argv){
//handshake
handshake_server(socket);
int client_in = recv_fd(socket);
int client_out = recv_fd(socket);
int client_err = recv_fd(socket);
dup2(client_in, STDIN_FILENO); //STDIN_FILENO = 0
dup2(client_out, STDOUT_FILENO); //STDOUT_FILENO = 1
dup2(client_err, STDERR_FILENO); //STDERR_FILENO = 2
//change current directory
chdir("/");
char* env[] = {SHELL_ENV, PATH_ENV, NULL};
char* shell[] = {DEFAULT_SHELL, NULL};
execve(shell[0], shell, env);
//expect no return from execve
//only if execve fails
ERRMSG("Failed on launching shell: ");
ERRMSG(strerror(errno));
ERRMSG("\n");
close(socket);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//start the daemon and keep waiting for connections from client
void run_daemon( char** argv) {
if (getuid() != 0) {
ERRMSG("Daemon require root privilege\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//get a UNIX domain socket file descriptor
int socket = creat_socket();
//wait for connection
//and handle connections
int client;
while ((client = accept(socket, NULL, NULL)) > 0) {
if (0 == fork()) {
close(socket);
ERRMSG("Child process start handling the connection\n");
exit(child_process(client,argv));
child_process(client, argv);
}
else {
close(client);
}
}
//expect daemon never end execution
//unless socket failed
ERRMSG("Daemon quits: ");
ERRMSG(strerror(errno));
ERRMSG("\n");
close(socket);
close(client);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//try to connect to the daemon to determine whether it is running
bool detect_daemon() {
struct sockaddr_un sun;
//create socket fd
int socket_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (socket_fd < 0) {
ERRMSG("failed to create socket fd\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//set socket fd
if (fcntl(socket_fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC)) {
ERRMSG("failed on fcntl\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//set sun
memset(&sun, 0, sizeof(sun));
sun.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strncpy(sun.sun_path, SERVER_LOC, sizeof(sun.sun_path));
//connect to server
//return false if connection failed (daemon is not running)
if (0 != connect(socket_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&sun, sizeof(sun))) {
return false;
}
//close the socket and return true if connection succeeded (daemon is running)
close(socket_fd);
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// 返回0表示是子进程运行的fork,判断如果守护进程没有运行,则运行守护进程
//initialize the daemon if not running
if (!detect_daemon())
run_daemon(argv);
}
else {
argv[0] = APP_PROCESS;
execve(argv[0], argv, environ);
}
}
mysu.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h> //socket() bind() listen() accept() AF_UNIX
#include <fcntl.h> //fcntl()
#include <string.h> //strerror()
#include <errno.h> //errno
#include <sys/un.h> //struct sockaddr_un
#include "../socket_util/socket_util.h"
#include "../server_loc.h"
#define ERRMSG(msg) fprintf(stderr, "%s", msg)
#define DEFAULT_SHELL "/system/bin/sh"
#define SHELL_ENV "SHELL=" DEFAULT_SHELL
#define PATH_ENV "PATH=/system/bin:/system/xbin"
//try to connect to the server and get a socket file descriptor
int config_socket() {
struct sockaddr_un sun;
//create socket fd
int socket_fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (socket_fd < 0) {
ERRMSG("failed to create socket fd\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//set the socket file descriptor
//with flag FD_CLOEXEC, socket_fd will stay valid through fork()
//but will be destroyed by all exec family functions (e.g. execve())
if (fcntl(socket_fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC)) {
ERRMSG("failed on fcntl\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//set struct sockaddr_un
/*
struct sockaddr_un {
sa_family_t sun_family; //AF_UNIX
char sun_path[108]; //pathname
};
*/
memset(&sun, 0, sizeof(sun));
sun.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strncpy(sun.sun_path, SERVER_LOC, sizeof(sun.sun_path));
//connect to server
if (0 != connect(socket_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&sun, sizeof(sun))) {
ERRMSG("failed to connect server\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return socket_fd;
}
//try to connect the daemon server
//pass stdin, stdout, stderr to server
//hold the session to operate the root shell created and linked by server
int connect_daemon() {
//get a socket
int socket = config_socket();
//do handshake
handshake_client(socket);
ERRMSG("sending file descriptor \n");
fprintf(stderr,"STDIN %d\n",STDIN_FILENO);
fprintf(stderr,"STDOUT %d\n",STDOUT_FILENO);
fprintf(stderr,"STDERR %d\n",STDERR_FILENO);
send_fd(socket, STDIN_FILENO); //STDIN_FILENO = 0
send_fd(socket, STDOUT_FILENO); //STDOUT_FILENO = 1
send_fd(socket, STDERR_FILENO); //STDERR_FILENO = 2
//hold the session until server close the socket or some error occurs
//in my design, server should not send things back through socket after handshake
//read() function will block the process, thus we hold the session
//if the socket is closed, read() will return 0
//or error occurs, read() will return a negative integer
char dummy[2];
ERRMSG("2 \n");
int flag = 0;
do {
flag = read(socket, &dummy, 1);
} while (flag > 0);
ERRMSG("3 \n");
close(socket);
//print out error message if has
if (flag < 0) {
ERRMSG("Socket failed on client: ");
ERRMSG(strerror(errno));
ERRMSG("\n");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//if not root
//connect to root daemon for root shell
if (getuid() != 0 && getgid() != 0) {
ERRMSG("start to connect to daemon \n");
return connect_daemon();
}
//if root
//launch default shell directly
char* shell[] = {"/system/bin/sh", NULL};
execve(shell[0], shell, NULL);
return (EXIT_SUCCESS);
}