数据包嗅探
socket接收数据包
以下为一个UDP服务器程序,INADDR_ANY表示socket绑定到本机所有ip地址
// udp_server.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
void main()
{
struct sockaddr_in server;
struct sockaddr_in client;
int clientlen;
char buf[1500];
int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
memset((char *) &server, 0, sizeof(server));
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server.sin_port = htons(9090);
if(bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof(server)) < 0)
perror("ERROR on binding");
while(1){
bzero(buf, 1500);
recvfrom(sock, buf, 1500-1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &clientlen);
printf("%s\n", buf);
}
close(sock);
}
首先起UDP服务:

接着宿主机往虚拟机9090端口发数据:

服务端收到数据:

原始套接字数据包嗅探
以上程序只能接收发送给它的数据包,如果目的ip地址是其他设备或者目的端口号不是由该程序注册的端口的话,就无法接收数据包。
而嗅探器程序需要能够捕捉网络中传输的所有数据包,无论其ip地址和端口号是什么,可以由一种称为原始套接字(raw socket)的
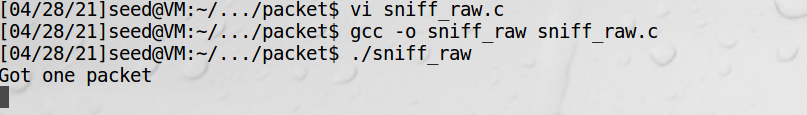
特殊socket实现,如下:
// sniff_raw.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/if_packet.h>
#include <net/ethernet.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int main()
{
int PACKET_LEN = 512;
char buffer[PACKET_LEN];
struct sockaddr saddr;
struct packet_mreq mr;
int sock = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL)); // 创建raw socket
mr.mr_type = PACKET_MR_PROMISC; // 设置为混杂模式
setsockopt(sock, SOL_PACKET, PACKET_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, &mr, sizeof(mr));
while(1)
{
int data_size = recvfrom(sock, buffer, PACKET_LEN, 0, &saddr, (socklen_t*)sizeof(saddr));
if(data_size)printf("Got one packet\n");
sleep(1);
}
close(sock);
return 0;
}
Warning
书上不加sleep会导致刷屏
原始套接字和普通套接字的区别
普通套接字当内核接收到数据包时,它会通过网络协议栈传递数据包,并最终将数据包的载荷(payload)通过socket传递
给应用程序。
对于原始套接字,内核首先会向socket(和它的应用)传递数据包的一份拷贝,包括链路层头部等信息,然后再进一步将数据
包传递给协议栈。raw socket不会拦截数据包,只是得到了数据包的一份拷贝。
int sock = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL));
ETH_P_ALL表示所有协议类型的数据包都应该被传递给raw socket。ETH_P_IP表示只有ip数据包传递给raw socket。 这个程序没有设置数据包过滤,如果过滤可以使用SO_ATTACH_FILTER选项来调用setsockopt
pcap(packet capture,数据包捕捉)API提供了一种跨平台、高效的数据包捕获机制。特点之一是提供了一个编译器,
使程序员可以用可读性较强的布尔表达式来指定过滤规则。编译器将表达式翻译成为内核可以利用的BPF伪代码。
libpcap和Winpcap分别是unix和windows中的pcap API。在Linux中,pcap是用raw socket实现的。
查找网络设备
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *dev, errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
dev = pcap_lookupdev(errbuf);
if (dev == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't find default device: %s\n", errbuf);
return(2);
}
printf("Device: %s\n", dev);
return(0);
}
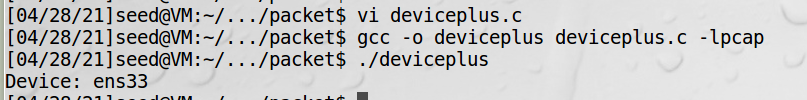 pcap实验要做成功,这个程序一定要能成功获取到网络设备
pcap实验要做成功,这个程序一定要能成功获取到网络设备
Warning
用vagrant生成的虚拟机用这个程序无法获取网络设备,可能跟多网卡有关。这整个章节要换seed lab提供的虚拟机 镜像来做实验。
pcap API实现数据包嗅探
#include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
printf("Got a packet\n");
}
int main()
{
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
struct bpf_program fp;
char filter_exp[] = "port 23";
bpf_u_int32 net;
handle = pcap_open_live("ens33", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device ens33: %s\n", errbuf);
return(2);
}
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return(2);
}
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return(2);
}
pcap_loop(handle, -1, got_packet, NULL);
pcap_close(handle);
return 0;
}
pcap_open_live("ens33", BUFSIZ, 1, 100, errbuf);
这行是开启有效pcap会话,eth1是网络设备名,实际ifconfig替换成自己的,1表示开启混杂模式
pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net); //编译过滤表达式
pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp); // 把编译好的BPF过滤器交给内核
这两行是设置过滤器,BPF过滤器是底层语言写的,开发人员很难阅读,pcap API提供的编译器可以将布尔表达式 转换成底层BPF程序。
pcap_loop(handle, -1, got_packet, NULL);
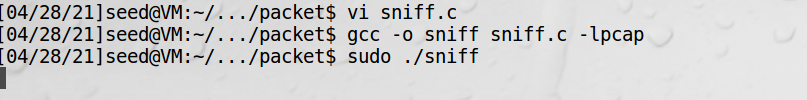
捕获数据包,第二个参数是希望捕获多少个数据包,-1表示永远不停止,第三个是回调函数 编译sniff.c的命令如下:
gcc -o sniff sniff.c -lpcap
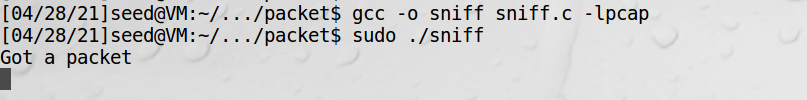
启动程序等待抓包:
宿主机发包:
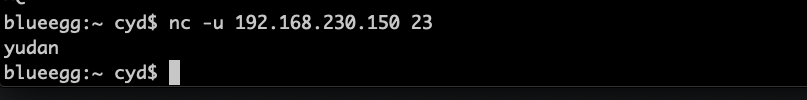
虚拟机显示收到包:
Warning
书上这个程序有两个问题,一是filter_exp设置成ip proto icmp不好测试,二是没有判断是否成功,会导致 程序经常崩溃而不知道问题所在。
pcap抓包可以参考pcap抓包
这个实验一定要做成功,否则后面没法继续。
处理捕获的数据包
void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
printf("Got a packet\n");
}
接收数据包的回调函数中,第三个参数packet是一个指针,指向存储在缓冲区中的数据包。指针类型是unsigned char,说明 缓冲区内存会被当做字符序列进行处理,是有结构的。c语言一个高效处理方法是使用结构体和类型转换的概念。
Pcap过滤器实例
dst host 10.0.2.5 只捕获目的ip地址为10.0.2.5的数据包
src host 10.0.2.6 只捕获源ip地址为10.0.2.6的数据包
host 10.0.2.6 and src host port 9090 只捕获源或目的ip地址为10.0.2.6,并且源端口号为9090的数据包
proto tcp 只捕获TCP数据包
Note
数据包实际上是一个以太网帧
// sniff_improved.c
#include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
struct ethheader
{
u_char ether_dhost[6];
u_char ether_shost[6];
u_short ether_type;
};
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, // ip头长度
iph_ver:4; // ip版本
unsigned char iph_tos; // 服务版本
unsigned short int iph_len; // ip包长度
unsigned short int iph_ident;
unsigned short int iph_flag:3,
iph_offset:13;
unsigned char iph_ttl;
unsigned char iph_protocol;
unsigned short int iph_chksum;
struct in_addr iph_sourceip;
struct in_addr iph_destip;
};
void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
if (ntohs(eth->ether_type) == 0x0800){
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
printf(" From: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip));
printf(" To: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip));
switch(ip->iph_protocol){
case IPPROTO_TCP:
printf(" Protocol: TCP\n");
return;
case IPPROTO_UDP:
printf(" Protocol: UDP\n");
return;
case IPPROTO_ICMP:
printf(" Protocol: ICMP\n");
return;
default:
printf(" Protocol: others\n");
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
struct bpf_program fp;
char filter_exp[] = "port 23";
bpf_u_int32 net;
handle = pcap_open_live("ens33", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device ens33: %s\n", errbuf);
return(2);
}
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return(2);
}
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return(2);
}
pcap_loop(handle, -1, got_packet, NULL);
pcap_close(handle);
return 0;
}
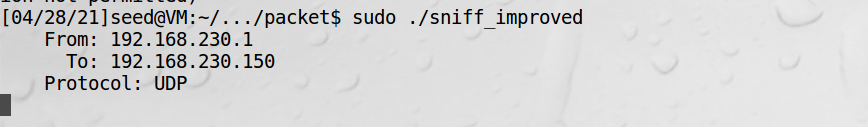
虚拟机起服务:
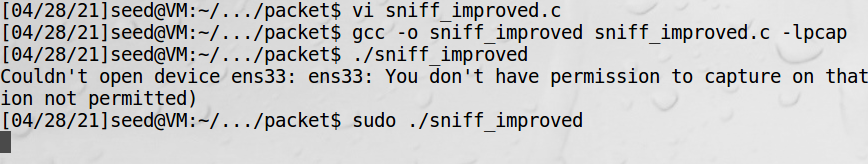
宿主机发包:

虚拟机收到包: